Difference between revisions of "Synonymy and length"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The number of synonyms of a word is indirectly associated with its length (if length is variable in the given language). This is the consequence of the fact that both length and synonymy depend on polysemy, the former in negative the latter in positive sense. The specification of meaning, i.e. reduction of polysemy, leads to a prolongation of the word (by affixation, compounding, reduplication etc.) and to the reduction of possible synonyms. Thus we have the scheme: | The number of synonyms of a word is indirectly associated with its length (if length is variable in the given language). This is the consequence of the fact that both length and synonymy depend on polysemy, the former in negative the latter in positive sense. The specification of meaning, i.e. reduction of polysemy, leads to a prolongation of the word (by affixation, compounding, reduplication etc.) and to the reduction of possible synonyms. Thus we have the scheme: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div align="center">[[image:Figur1_SaL.jpg]]</div> | ||
The only hypothesis set up and tested is that of Wimmer and Altmann (2001a) concerning Italian synonyms. Corroborating results brought Uhlířová (2001a) for Czech and Rottmann (2001a) for Russian, Bulgarian, Polish and Ukrainian. | The only hypothesis set up and tested is that of Wimmer and Altmann (2001a) concerning Italian synonyms. Corroborating results brought Uhlířová (2001a) for Czech and Rottmann (2001a) for Russian, Bulgarian, Polish and Ukrainian. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div align="center">[[image:Grafik1_SaL.jpg]]</div> | <div align="center">[[image:Grafik1_SaL.jpg]]</div> | ||
Revision as of 10:30, 3 July 2006
1. Problem and history
The number of synonyms of a word is indirectly associated with its length (if length is variable in the given language). This is the consequence of the fact that both length and synonymy depend on polysemy, the former in negative the latter in positive sense. The specification of meaning, i.e. reduction of polysemy, leads to a prolongation of the word (by affixation, compounding, reduplication etc.) and to the reduction of possible synonyms. Thus we have the scheme:
The only hypothesis set up and tested is that of Wimmer and Altmann (2001a) concerning Italian synonyms. Corroborating results brought Uhlířová (2001a) for Czech and Rottmann (2001a) for Russian, Bulgarian, Polish and Ukrainian.
More complex dependencies have not been tested as yet.
2. Hypothesis
The number of synonyms of a word is a function of its length (or vice versa) .
3. Derivation
Using the unified theory (see § 4.1, Example 1) we assume that the relative rate of change of synonymy is proportional to the relative rate of change of length while polysemy plays an intermediary role expressed by a constant c, i.e. (y = synonymy, x = word length)
(1) 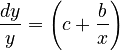
resulting in
(2)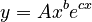 .
.
This concerns, of course, the mean number of synonyms for all words of a given length.
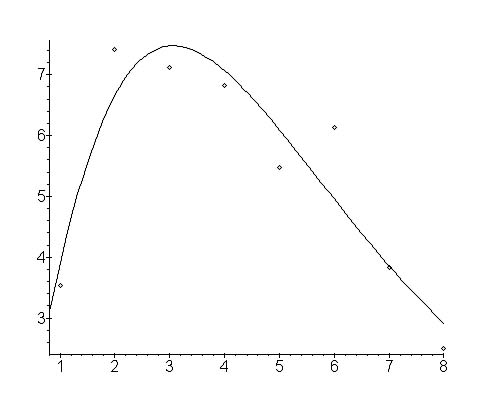
Example. Length and synonymy in Italian
Wimmer and Altmann (2001a) took a sample from the Italian dictionary by P. Stopelli, Sinonimi e Contrari con generici, Spezifici, Analoghi, Inversi. (Milano, Garzanti 1998) and found the results presented in Table 1 and Figure 1. As can be seen, the curve is here concave.
Further testing is necessary. It must be noted that in the observed data only in one case (Bulgarian, cf. Rottmann 2001a) the value of x = 1 was greater than the other ones.
4. Authors: U. Strauss, G. Altmann
5. References
Rottmann, O. (2001a). On the “second law of synonymy”: observations in Russian, Bulagrian, Polish and Ukrainian. In: Ondrejovič, S., Považaj, M. (eds.), Lexicographica ´99: 251-257. Bratislava: Veda
Uhlířová, L. (2001a). Kolik je v češtine synonym? (K dynamické stabilitě v systému lexikálních synonym). In: Ondrejovič, S., Považaj, M. (eds.), Lexicographica ´99: 237-250. Bratislava: Veda.
Wimmer, G., Altmann, G. (2001a). Two hypotheses on synonymy. In: Ondrejovič, S., Považaj, M. (eds.), Lexicographica ´99: 218-225. Bratislava: Veda.